The rapid advancement of technology in recent years has led to a significant shift in how we perceive transportation. Among the most talked-about innovations is the concept of self-driving cars, which promises to revolutionize the way we travel. As we stand on the brink of this future, it is crucial to dissect the reality behind autonomous vehicles and the hype that surrounds them.
While proponents paint an optimistic picture of a world where self-driving cars reduce accidents, ease congestion, and provide mobility for those unable to drive, skeptics raise valid concerns about safety, regulatory challenges, and the current limitations of the technology. The disparity between the vision of fully autonomous vehicles and their actual implementation often leaves consumers questioning what is achievable in the near term.
In this article, we will explore the current state of self-driving technology, assess the potential benefits and drawbacks, and clarify the distinctions between the promise of a self-driving future and the present-day realities. By examining these factors, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of where we stand today and what to expect in the journey ahead.
Evaluating Current Technologies in Autonomous Vehicles
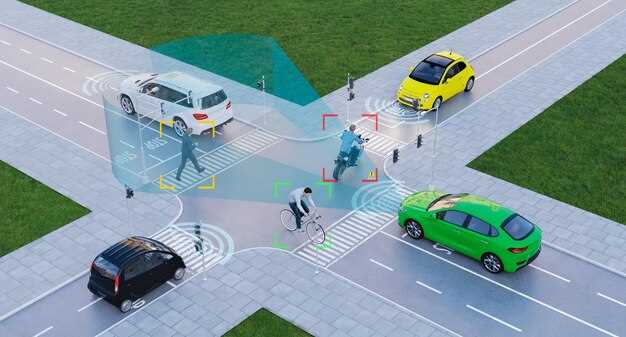
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) utilize a combination of advanced technologies to navigate and operate without human intervention. Key components include sensors, software algorithms, and data processing systems that work together to create a robust driving experience.
Firstly, sensors play a critical role in enabling AVs to perceive their environment. Lidar, radar, and cameras are commonly used to gather real-time data about surrounding objects, road conditions, and potential hazards. Lidar systems use laser pulses to determine distances, creating a detailed 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings. This allows for accurate detection of obstacles, even in low-light conditions.
Secondly, software algorithms are essential for the interpretation of the data collected by sensors. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are at the core of these algorithms, allowing vehicles to make informed decisions based on predictive modeling and pattern recognition. This capability enables autonomous systems to understand complex driving situations, such as merging into traffic or navigating through pedestrian-heavy areas.
Moreover, communication technologies enhance the performance of autonomous vehicles. Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication facilitates interaction between vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians. This connectivity improves situational awareness and enables vehicles to anticipate movements of other road users, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Furthermore, robust testing and validation processes are crucial for ensuring the reliability of autonomous technologies. Simulation environments and closed-course tests are frequently used to evaluate the performance of AVs in diverse scenarios. Real-world testing enables manufacturers to refine their systems and address potential safety concerns before deploying vehicles on public roads.
In conclusion, the landscape of autonomous vehicles is shaped by a multitude of technologies that synergize to create a safe and efficient driving experience. Continuous advancements in sensor capabilities, AI-driven algorithms, and communication systems are pivotal in the evolution of autonomous driving. Evaluating these technologies provides insight into the future of transportation and the potential for fully autonomous systems.
Impact of Self-Driving Cars on Urban Mobility
Self-driving cars are poised to redefine urban mobility by introducing a new era of transportation that prioritizes efficiency, safety, and accessibility. The future of urban landscapes will likely be shaped by the integration of autonomous vehicles, fundamentally altering how people navigate cities.
One significant impact is the potential reduction in traffic congestion. Autonomous vehicles can communicate with one another and traffic management systems, optimizing routes and minimizing delays. This coordinated movement could lead to smoother traffic flow, ultimately decreasing travel times in urban centers.
Furthermore, self-driving cars have the potential to reduce parking demands. With the advent of autonomous ride-sharing services, the need for vast parking lots may diminish, freeing up valuable urban land for parks, housing, and commercial spaces. As a result, cities could transform into more pedestrian-friendly environments, enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
Another critical aspect is safety. Autonomous vehicles are designed to eliminate human error, which is responsible for a significant percentage of traffic accidents. The reduction in collisions could lead to lower injury and fatality rates, fostering a safer urban environment.
Moreover, self-driving technology may improve mobility for individuals with disabilities and the elderly, who may rely on private transportation. Autonomous vehicles can offer tailored solutions, ensuring inclusivity and providing access to those who face challenges with conventional driving.
Despite these positive prospects, challenges such as regulatory frameworks, infrastructure adaptation, and public acceptance must be addressed. Policymakers need to create guidelines that support the safe deployment of autonomous vehicles while ensuring equitable access to emerging technologies. Urban planners must reimagine city designs to accommodate these changes, focusing on integrated transportation systems.
In summary, the advancement of self-driving cars is set to have a profound impact on urban mobility. As cities evolve, the integration of autonomous vehicles could enhance efficiency, safety, and accessibility, leading to a more sustainable and vibrant urban future.
Legal and Ethical Challenges of Autonomous Driving
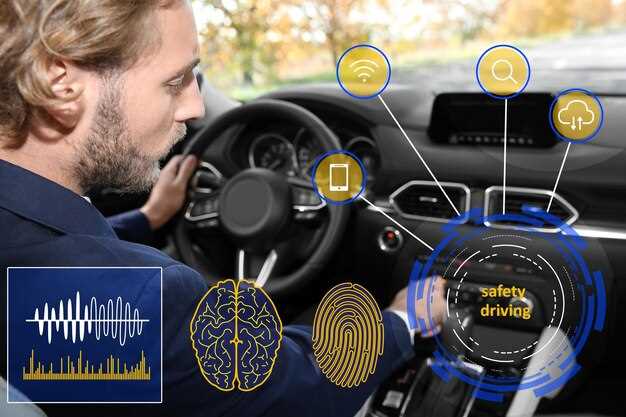
The introduction of autonomous vehicles presents a range of legal and ethical challenges that must be addressed to ensure their safe integration into society. One of the most pressing legal challenges involves liability in the event of an accident. In traditional driving scenarios, determining fault is relatively straightforward. However, with autonomous cars, the question of responsibility becomes more complex. Is it the manufacturer, the software developer, or the car owner who is liable when an autonomous vehicle fails to react appropriately? Establishing clear legal frameworks is essential for resolving these issues.
Another significant legal consideration pertains to regulation and standards. Autonomous vehicles rely on sophisticated technology and algorithms. As this technology evolves, regulatory bodies must keep pace by creating laws that govern their use. This includes ensuring compliance with safety standards and addressing issues such as data privacy, as autonomous vehicles collect vast amounts of data about their environment and passengers.
From an ethical standpoint, autonomous driving raises questions about decision-making in critical situations. For instance, if an accident is unavoidable, how should an autonomous vehicle prioritize the safety of its occupants versus that of pedestrians? This dilemma echoes classic ethical theories, such as utilitarianism and deontological ethics, challenging developers to program vehicles that can make morally sound decisions.
Furthermore, there is a concern about equity in access to autonomous technology. As the technology advances, disparities may arise between those who can afford autonomous vehicles and those who cannot. Ensuring that all segments of the population benefit from autonomous driving technology is vital in creating a fair society.
In summary, the path to widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is fraught with legal and ethical challenges. Addressing issues of liability, regulation, ethical decision-making, and equitable access will be crucial for fostering public trust and ensuring the successful implementation of this transformative technology.



